In the realm of home entertainment and professional AV setups, HDMI cables are the lifelines that transmit high-definition audio and video signals between devices. While HDMI technology has significantly improved over the years, one challenge remains prevalent: signal degradation over long cable lengths. As consumers and professionals strive for larger displays and more intricate setups, understanding the factors contributing to signal loss and implementing strategies to mitigate them becomes crucial. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of HDMI cable length and signal degradation, exploring methods to preserve signal integrity in long-distance installations.
Understanding Signal Degradation
Signal degradation occurs when the quality of the HDMI signal deteriorates as it travels through the cable. This degradation is primarily caused by attenuation, a phenomenon where the signal weakens over distance due to resistance and other factors. As the length of the HDMI cable increases, so does the potential for signal loss, resulting in pixelation, flickering, or even complete loss of the audiovisual signal.
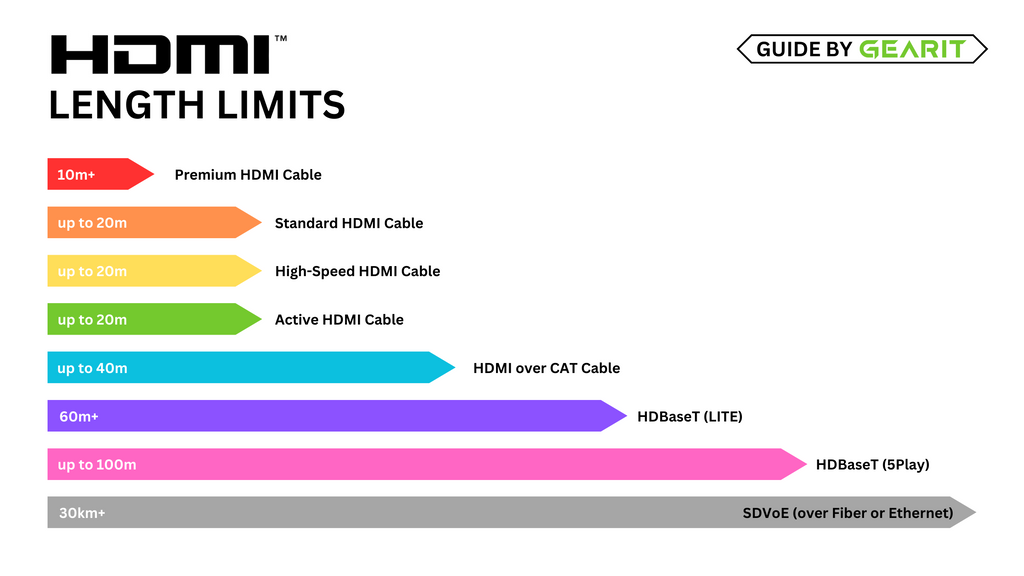
Factors Contributing to Signal Loss
Several factors contribute to signal degradation in long HDMI cable runs:
Cable Length: The longer the HDMI cable, the greater the signal loss. This is primarily due to the increased resistance and capacitance along the cable, which attenuates the signal over distance.
Cable Quality: The quality of the HDMI cable itself plays a significant role in signal integrity. Higher-quality cables typically feature better shielding, thicker conductors, and superior construction, reducing the likelihood of signal loss.
Resolution and Bandwidth: Higher resolutions, such as 4K and beyond, require more bandwidth to transmit the signal. Longer cable runs can exacerbate signal degradation, particularly at higher resolutions and refresh rates.
Interference: External factors like electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) can disrupt the HDMI signal, leading to degradation or signal loss. Shielding and proper cable management can help mitigate interference.
Mitigating Signal Loss in Long-Distance Installations
While signal degradation is an inevitable consequence of long HDMI cable runs, several strategies can help mitigate its effects:
Choose High-Quality Cables: Invest in high-quality HDMI cables with robust construction, thick conductors, and effective shielding. While they may be more expensive upfront, they can provide better signal integrity over longer distances.
Use Signal Boosters/Repeaters: HDMI signal boosters or repeaters amplify the signal at intervals along the cable run, compensating for losses and maintaining signal strength over long distances.
Active Optical Cables (AOC): AOCs utilize optical fibers to transmit HDMI signals, offering greater bandwidth and reduced signal loss compared to traditional copper cables. They are particularly effective for ultra-long cable runs.
Consider Fiber Optic Solutions: Fiber optic HDMI cables offer unparalleled signal integrity over long distances, thanks to their immunity to electromagnetic interference and low attenuation. While they may be more expensive, they are ideal for demanding installations.
Proper Cable Management: Ensure proper cable management practices to minimize stress on the HDMI cable and reduce the risk of signal loss due to physical damage or interference.
Conclusion
As consumers and professionals demand ever-larger displays and more intricate AV setups, understanding the challenges posed by HDMI cable length and signal degradation becomes paramount. By recognizing the factors contributing to signal loss and implementing strategies to mitigate them, it's possible to maintain optimal signal integrity over long-distance HDMI installations. Whether through high-quality cables, signal boosters, or fiber optic solutions, preserving the integrity of the audiovisual signal ensures a seamless and immersive viewing experience for users across various applications.






















































